User Management
User Management in simpleBillBook allows you to create and manage user accounts, assign roles and permissions, and control who has access to your organization's data. Proper user management ensures security, accountability, and efficient collaboration across your team.
Overview of User Management
User Management helps you:
- Create User Accounts: Add team members to the system
- Assign Roles: Control what each user can access and do
- Manage Access: Grant or revoke system access as needed
- Track Activity: Know who performed specific actions
- Maintain Security: Ensure only authorized personnel have access
Viewing Users
To view all users:
- Navigate to Manage Users → Users from the main sidebar
- You'll see a table listing all user accounts in your organization
 Figure 1: Users list showing all user accounts
Figure 1: Users list showing all user accounts
Users Table Columns:
User Information:
- Name: Full name of the user
- Email: User's email address (used for login)
- Role: Assigned role(s) determining permissions
Interface Elements:
- Type to search: Search functionality for finding specific users
- All dropdown: Filter users by role, status, or other criteria
- Empty State: "No results" message when no users exist
- Create +: Button to create new users (inferred from previous patterns)
Creating a New User
Step 1: Access User Creation
From the users page, click Create + or similar button to add a new user.
Step 2: Fill User Details
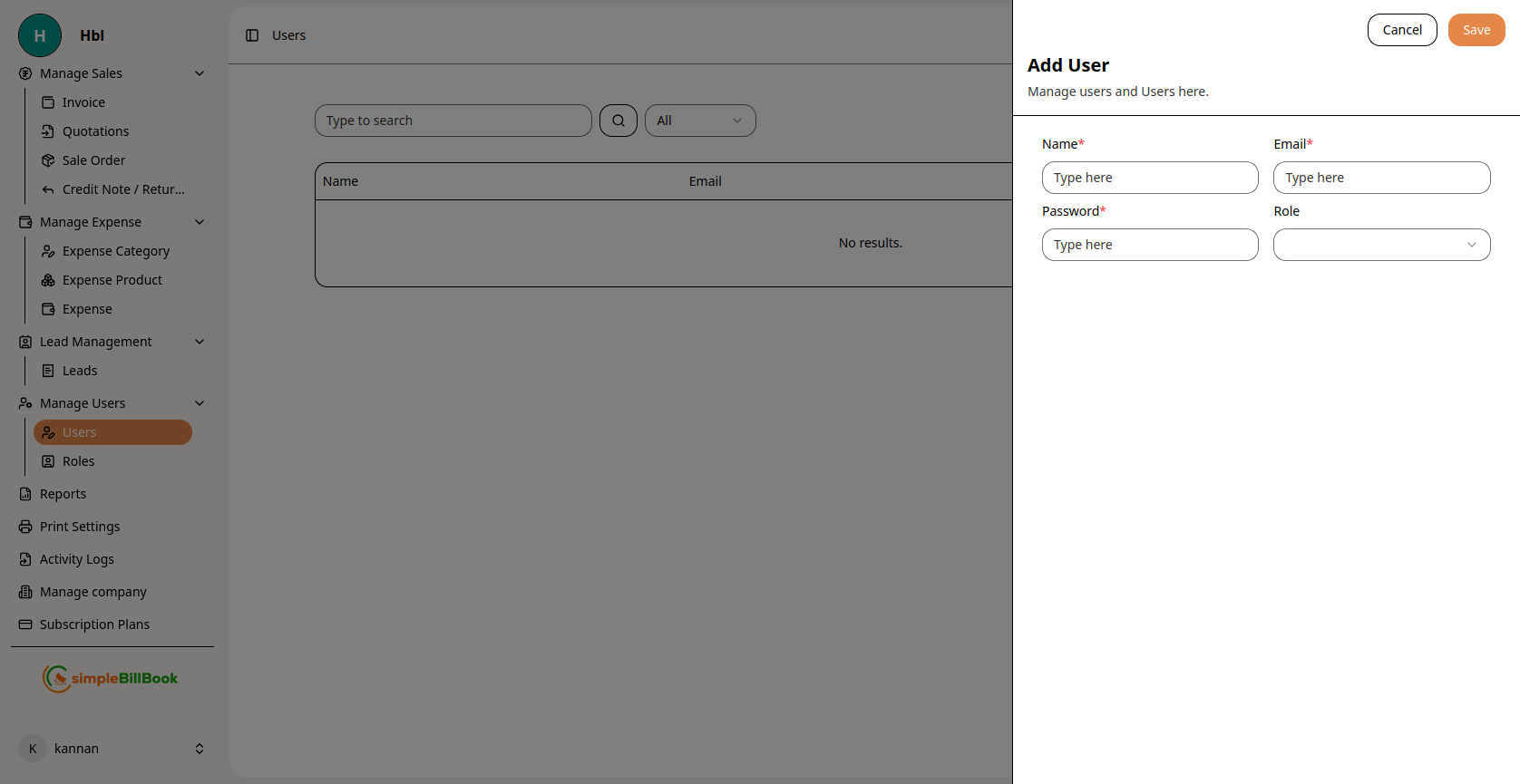 Figure 2: Form for creating new users
Figure 2: Form for creating new users
Required Information:
- Name*: Full name of the user (required)
- Email*: Email address for login and notifications (required)
- Role*: Select role from dropdown to assign permissions (required)
Optional Information:
- Phone: Contact phone number
- Department: Department or team
- Employee ID: Internal employee identifier
- Joining Date: Date user started
- Reports To: Manager or supervisor
- Location: Physical location or branch
Account Settings:
- Username: May be auto-generated from email or custom
- Password: Set initial password or send invitation email
- Status: Active/Inactive (defaults to Active)
- Two-Factor Authentication: Optional security setting
Step 3: Save User
- Click Save to create the user account
- User receives notification/credentials based on settings
- User appears in the users list and can log in
User Roles and Permissions
Role Assignment:
- Each user must be assigned at least one role
- Roles determine what the user can view, create, edit, and delete
- Users may have multiple roles (permissions combine)
Common User Roles:
| Role | Typical Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Admin | Full system access, user management, configuration |
| Manager | Oversee operations, approvals, reporting |
| Sales Representative | Customer management, quotations, sales orders |
| Purchase Officer | Vendor management, purchase orders, stock |
| Accountant | Financial transactions, expense tracking, reports |
| Warehouse Staff | Inventory management, stock adjustments |
| Viewer | Read-only access for auditors or executives |
User Status Management
Active Users:
- Can log in to the system
- Have full access based on assigned roles
- Appear in selection lists and reports
- Can perform permitted actions
Inactive Users:
- Cannot log in to the system
- Preserve historical data (created by, modified by)
- Do not appear in active user selections
- Can be reactivated if needed
Status Change Reasons:
- Employee Resignation: Set to inactive
- Role Change: Update role or create new account
- Leave of Absence: Temporarily deactivate
- Contract End: Deactivate contractor accounts
- Security Concerns: Immediate deactivation
Best Practices for User Management
1. Principle of Least Privilege
- Grant minimum permissions needed for job function
- Start with restrictive roles, add as needed
- Regularly review and revoke unnecessary access
2. Timely User Updates
- Create accounts promptly for new hires
- Deactivate immediately when employees leave
- Update roles when responsibilities change
- Remove temporary access when no longer needed
3. Consistent Naming Conventions
- Use full legal names for clarity
- Company email addresses as primary identifier
- Avoid duplicate or similar usernames
4. Secure Authentication
- Enforce strong password policies
- Implement two-factor authentication for sensitive roles
- Regular password rotation requirements
- Single Sign-On (SSO) integration if available
5. Documentation
- Maintain user-role matrix documentation
- Document approval process for new accounts
- Keep records of access reviews
6. Regular Audits
- Quarterly review of all active users
- Verify appropriate role assignments
- Remove orphaned or unused accounts
- Document audit findings and actions
User Lifecycle Management
Onboarding Process:
- Request: Manager requests new user account
- Approval: Authorized approver validates request
- Creation: Administrator creates user account
- Role Assignment: Appropriate roles assigned
- Credential Delivery: User receives login information
- Training: User learns system functionality
- Verification: Confirm user can access required features
Role Change Process:
- Notification: HR or manager communicates role change
- Review: Evaluate new permission requirements
- Update: Modify role assignments
- Verify: Confirm appropriate access levels
- Document: Record change for audit trail
Offboarding Process:
- Notification: HR or manager initiates offboarding
- Immediate Deactivation: Disable user access
- Data Handover: Transfer ownership of active records
- Access Removal: Remove from all systems
- Final Verification: Confirm account is inactive
- Documentation: Record offboarding date and reason
Integration with Other Modules
Roles and Permissions:
- Role Assignment: Users inherit permissions from roles
- Custom Roles: Create roles for specific user groups
- Permission Boundaries: Define what users can access
Activity Logs:
- User Tracking: Every action is logged with user information
- Audit Trail: Know who created, modified, or deleted records
- Compliance: Meet regulatory requirements for accountability
Reports:
- User Activity Reports: Track user login and activity
- Permission Reports: Document user access levels
- Productivity Metrics: User performance analysis
Notifications:
- Email Alerts: Users receive system notifications
- Task Assignments: Work items assigned to specific users
- Approval Requests: Notifications for pending approvals
Common Scenarios and Solutions
Scenario 1: New Employee Joining
Solution:
- Create user account before start date
- Assign role matching job responsibilities
- Send welcome email with login instructions
- Schedule training session
Scenario 2: Employee Resignation
Solution:
- Deactivate account on last working day
- Transfer open tasks to another user
- Document account closure
- Preserve user records for historical data integrity
Scenario 3: Forgotten Password
Solution:
- Use "Forgot Password" self-service if enabled
- Administrator can trigger password reset
- Temporary password with forced change on login
Scenario 4: Multiple Users Share Account
Solution:
- Create individual accounts for each person
- Assign appropriate roles individually
- Train on proper account usage
- Audit shared account usage and eliminate practice
Scenario 5: Contractor Access
Solution:
- Create account with clear expiration date
- Assign limited, role-appropriate permissions
- Set calendar reminder for access review
- Deactivate promptly at contract end
Scenario 6: User Needs Temporary Higher Access
Solution:
- Create temporary role with additional permissions
- Assign temporarily with expiration date
- Document justification and approval
- Auto-revoke at specified date
Reports and Analytics
Available User Reports:
- Active Users Report: All currently active user accounts
- User-Role Matrix: Mapping of users to assigned roles
- Inactive Users: Users deactivated within a period
- User Activity Summary: Login frequency and activity levels
- New Users: Users created within date range
- Permission Coverage: Access levels across organization
Key Metrics to Monitor:
- Total Active Users: Number of users currently accessing system
- Users by Role: Distribution across different roles
- User Growth: Rate of new user creation
- Inactive Rate: Percentage of users deactivated
- Role Density: Average roles per user